Introduction
- Global System for Mobile Communications or GSM.
- a cellular digital telecommunications standard.
- first implemented in Finland in December, 1991.
- widely used in more than 200 nations and territories.
- shares frequency spectrum using time division multiple access (TDMA).
- supports digital services, SMS, and circuit-switched phone calls.
- uses SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) cards to identify users.
- incorporates security components like authentication and encryption.
- adapted to enable General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) and Enhanced GPRS (EDGE)'s higher data transfer rates.
- lays the groundwork for 3G (UMTS) and 4G (LTE) network technology.
Features
- Digital Cellular Technology
- Wide Coverage
- Compatibility
- SIM Card
- Roaming
- Voice and Data Services
- Security
- Call Management Features
- International Roaming
- Efficient Spectrum Utilization
- Interoperability
- Evolutionary Advancements
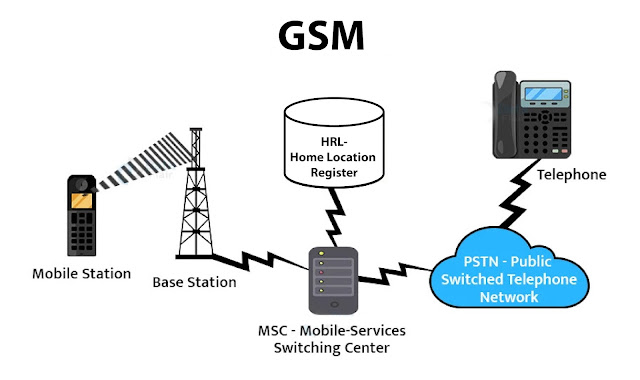
General figure of GSM working
Working
- GSM operates on the principle of dividing a geographic area into smaller cells to provide wireless coverage.
- A base station that provides service to each cell communicates with mobile devices in its coverage area.
- The mobile device contacts the closest base station whenever a user places a call.
- Call routing and network management are handled by the Mobile Switching Center (MSC), which is connected to by the base station.
- The MSC chooses the recipient's mobile device or another network as the call's destination and establishes a connection with it.
- Voice signals are encoded, compressed, and transferred as digital data via the GSM network while a call is in progress.
- GSM uses Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) to divide the frequency spectrum into time slots, allowing multiple users to share the same frequency.
- Each call is assigned a specific time slot within a frequency channel to prevent interference.
- GSM uses Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) to assign different frequency channels to different cells.
- The SIM card in the mobile device contains user-specific information and enables network authentication.
Advantages
- Global Standard
- Wide Coverage
- Interoperability
- Roaming Capability
- Efficient Spectrum Utilization
- Enhanced Voice Quality
- Data Services and Internet Access
- Security Features
- Support for Supplementary Services
- SIM Card Flexibility
- Evolutionary Advancements (3G, 4G)
Limitations
- Data transfer speed limit
- Voice-centric focus
- Limited multimedia support
- Limited carrying capacity in densely populated areas
- Lack of native support for IP-based services
- Limited channel capacity
- Mobile device battery life is limited
- Vulnerability to noise and interference
- Limited Support for Real-Time Applications